SUTURE REMOVAL – Purpose, Principle, Usual Timing, Factors Affecting, Types, General Instructions, Preliminary Assessment, Preparation of Patient and Environment, Procedure, Equipment and Post-Procedure Care

UPDATED 2024
Suture
removal is a process removing materials used to secure wound edges or body
parts together from healed wound without damaging newly formed tissue

The timing
of suture removal depends on the shape, size and location of the sutured
incision
The sutures
may be removed by the surgeons or by the surges regarding to the tropical
customs. In all cages, the surgeon gives the written order for the removal of
the sutures

PURPOSE
Sutures are
foreign bodies and if they are not removed they are capable of causing local
inflammation
PRINCIPLE
- Never pull the visible portion of the
suture through underlying tissue - Suture line is cleansed before and
after suture removal - No part of the stitch which is above
the skin level enter and contaminate the tissue under the skin
USUAL TIMING
- Scalp and free: 2-5 days
- Abdominal wounds: 7-10 days
- Lower limbs: 10-14 days
FACTORS AFFECTING THE SUTURE REMOVAL
- Type of suture
- Wound bedding
TYPES
- Removing staples: to remove staples,
the nurse simply inserts the tips of the staple remover under each wire
staples. Squeezes are center of the staple with the tips, freeing the staples
from the skin - Intermittent suture: the surgeon tied
each individual suture made in the skin - Continuous suture: it is the series
of sutures with only two knots - Retentions suture: they are placed
deeply than skin sutures
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
- Confirm the doctor’s order for the
removal of the sutures - The suture removal is done in
conjunction with the dressing change - When removal interrupted in sutures,
alternate one are removed first - Suture material left beneath the skin
acts as a foreign body and clients the inflammatory response - If wound dehiscence occurs during the
removal of sutures, inform the surgeon immediately - After removing the sutures, even if
the wound is dry, the small dressing is applied for the day or two to prevent
infection - If wound discharge occurs, the
patient should be instructed to contact the surgeon - Abdominal belts or many tailed
bandages may be applied as the abdomen after removal of abdominal sutures in
obese patients to prevent wound dehiscence and evisceration
PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT
- Check the physician’s order
- Assess the general candidates of the
patient - Check the specific precautions of any
- Check the consciousness of the
patient and his ability to follow instructions
PREPARATION OF PATIENT AND ENVIRONMENT
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- Provide privacy, if needed
- Clean the area before and after the
procedure
EQUIPMENT
- Water proof thrash bag
- Adjustable light
- Clean gloves, if the wound is dressed
- Sterile gloves
- Sterile forceps
- Normal saline solution
- Sterile gauze pads
- Antiseptic cleaning agent
- Sterile curve tipped suture scissors
- Povidone-iodine sponges
- Optional adhesive butterfly strips
and compound benzoin tincture or other skin protectant
PROCEDURE
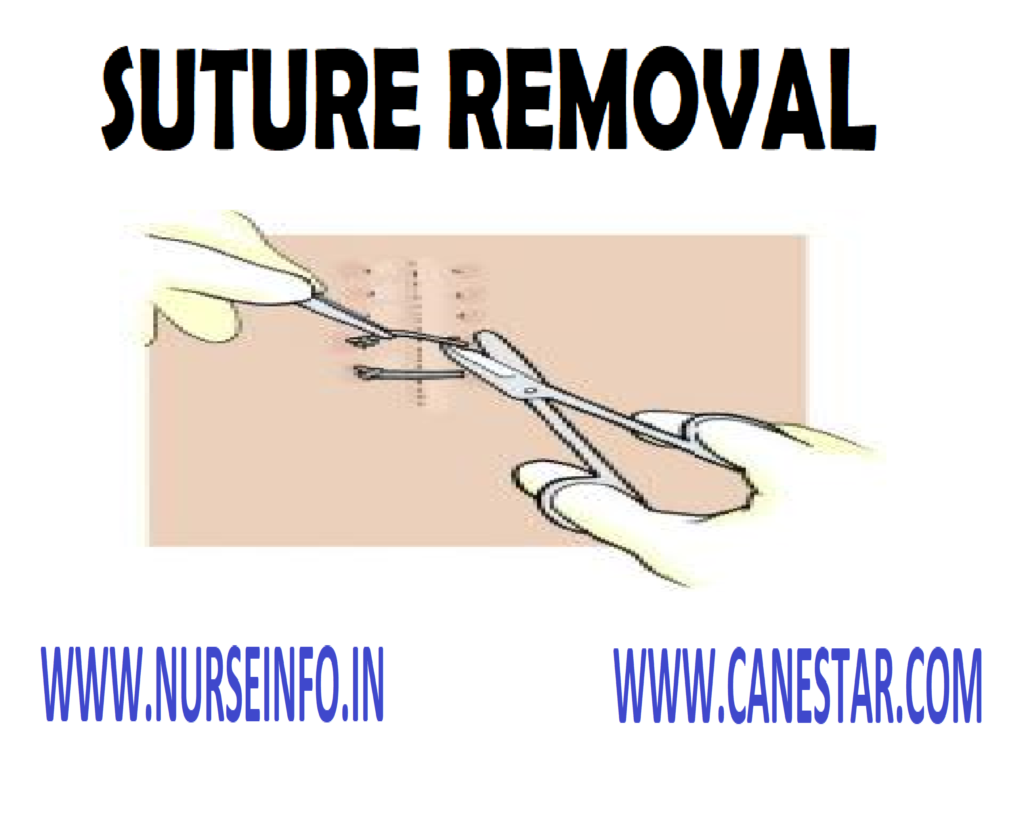
- To remove the interpreted sutures,
grasp the suture at the knot with a toothed forceps and pull it gently to
expose the portion of the stitch under the skin - Cut the suture with a sharp scissors
between the knot and the skin on one side either below the knot or opposite the
knot. The pull the thread out of one piece - The suture which is already above the
skin should not be drawn under the skin. After removal of sutures, every suture
should be examined for completeness. The number of suture’s shower be countered
before and after removal - Mattress intercepted sutures have no
threads underlying the skin. The visible part of the suture opposite the knot
should be cut and the suture is removed by putting in the direction of the knot - If a continuous suture is applied, it
is cut through, close at each skin orifice on one side and the cut sections are
removed through the opposite side by gentle traction
POST-PROCEDURE CARE
- After the removal of any suture we
showed clear the area - We can give dressing also the area to
prevent infection - Tell the patient to keep the area
clean - Document the status of the wound,
after suture removal




![First Aid (Quick Study Health) PDF Free Download [Direct Link]](https://bazarbiblio.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/First-Aid-Quick-Study-Health-PDF.jpg)
