BOWEL WASH – BOWEL ELIMINATION (Purpose, Contraindications, General Instructions, Methods Used, Solutions Used, Preliminary Assessment, Preparation of Patient and Environment, Equipment, Procedure and After Care)

UPDATED 2024
Bowel
elimination is a basic bodily function that most people carry out in private
and are often embarrassed to discuss publicly. Nurses will encounter patients
with bowel elimination issues in all areas of care. Knowledge and understanding
of both normal function and the problems that can occur with that process will
enable nurses to support and care for patients with bowel elimination problems

BOWEL WASH
Bowel wash
or colonic lavage or enteroclysis is defined as washing out colon with large
quantities of solution.

Bowel
irrigation or enteroclysis is defined as washing out of the colon after the
feces has been expelled by using large quantities of prescribed solution
PURPOSE
- To prepare for diagnostic examination
or before certain surgery - To relieve inflammation
- To stimulate peristalsis
- To supply fluid and electrolyte those
are absorbed from intestine - To dilute and remove toxic agents
- To reduce temperature in hyperpyrexia
- To relieve fecal incontinence
- To supply medications locally
- To clean the colon of feces, gas and
barium - To treat infection and other
pathological condition of colon
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Rectal infection
- Fistula in anus
- Painful and bleeding hemorrhoids
- Painful skin lesions around the anus
- Massive carcinoma or tumors of the
rectum - Loose sphincter
- Polypus and diverticula of the
intestine
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
- A cleaning enema should be given one
hour before the colon irrigation - The bladder should be emptied before
colonic irrigations - The temperature of the solution is
kept constant throughout the procedure - Allow only 200 to 300 ml of fluid to
run into the rectum at a time - Make sure that the return flow is not
blocked - Use a smooth and flexible rectal tube
and lubricate it well - Prevent air entry into the intestines
- Stop the procedure temporarily the
patient complaints of pain - Listen to the complaints of the
patient and should not ignore any discomfort however small they may be
METHODS USED FOR BOWEL IRRIGATION
- Funnel and catheter
- Y connection and a rectal tube
- Two tube method
SOLUTION USED
- Tap water
- Cold water
- Normal saline
- Sodium bicarbonate 1 to 2 %
- Antiseptic solution KNMO4
- Boric solution 1 to 2 %
- Tannic acid 1: 100
- Alum 1: 100
TEMPERATURE OF THE SOLUTION
- Cleaning purpose 104 degree F (40
degree Celcius) - Thermal effect 110 to 115 degree F
(43.3 to 46 degree celcius) - Reducing temperature 80 to 90 degree
F (27 to 32 degree celcius) amount of water used for bowl, irrigation is 2 to 3
liters or till the return flow is clear
PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT
Check
- Doctors order for any specific
precautions - Diagnosis of the patient
- General condition of the patient
- Self-care ability of the patient
- Mental status to follow instructions
- Any contraindications
- Need for any extra help
- Articles available in the unit
PREPARATION OF THE PATIENT AND ENVIRONMENT
- Explain the sequence of the procedure
- Arrange the articles at the bed side
- Provide privacy
- Place the Mackintosh and towel under
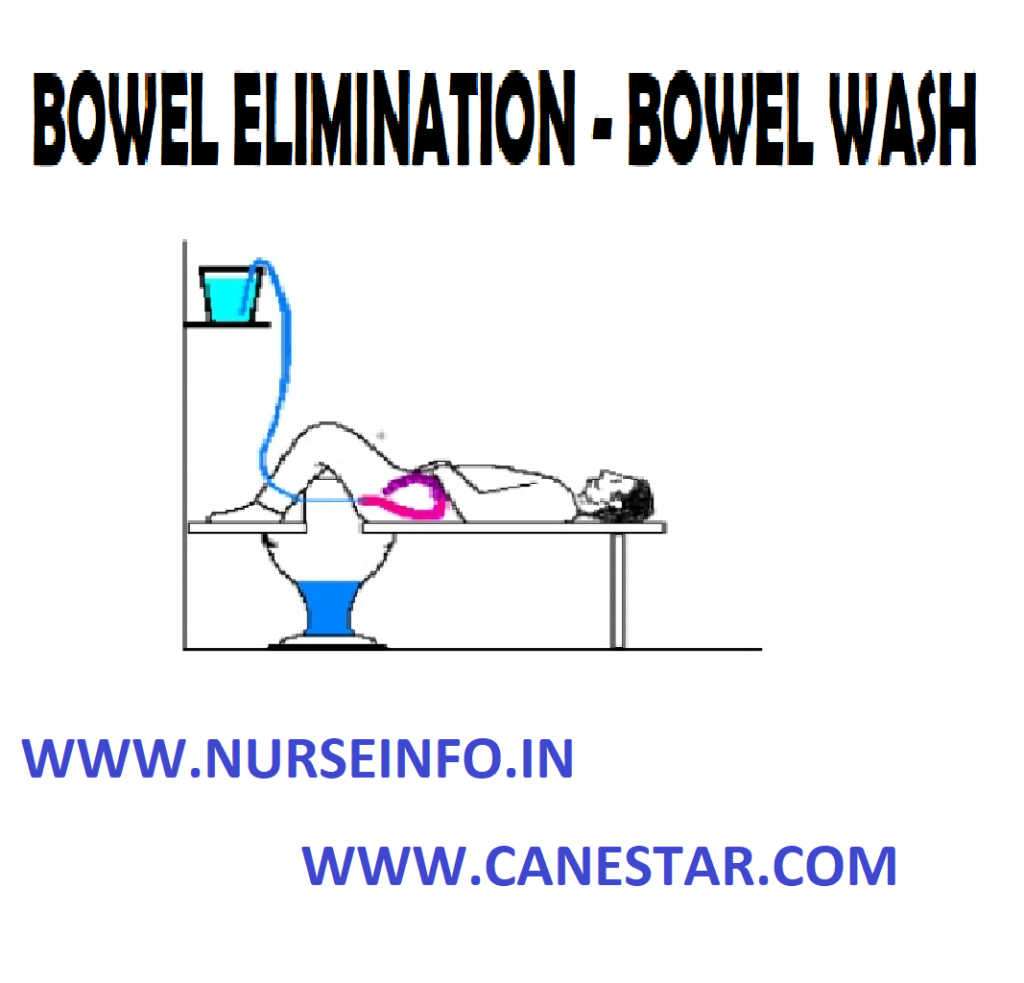
the patient - Place the patient in left later
position - Keep the bucket on a low stool or
receive the out flow of fluid - Remove the back rest and extra
pillows
EQUIPMENTS
A clean tray
containing
- Funnel and tubing with glass
connection - Mackintosh and towel
- Rectal tube placed in a kidney tray
- Vaseline
- Rag pieces in a container
- Hot and cold water in jugs
- Prescribed solution in jug
- Paper bag
- Bucket
- Toilet tray if needed
- Clean linen if needed
- Bath thermometer
PROCEDURE
- Wash hands thoroughly
- Prepare the solution at the required
temperature - Attach the tubing and the rectal tube
with the funnel, pour solution in it and check for any leakage - Lubricate the tip of the rectal tube
about 4 inches - Separate patient’s buttocks to
visualize anus clearly and insert tip of tube about 4 to 5 inches, while
patient takes deep breath - Lower funnel below level of rectum
and empty return flow into bucket - Fill funnel again. Pour 200 to 300 ml
of fluid each time. Raise funnel and allow fluid to run continuously. When 200
to 300 ml of fluid has gone in pinch tube before tunnel is completely. Lower
and invert tunnel over bucket and siphon fluid, noting characteristics of
return flow - Repeat this process, till return flow
is clear - Remove the rectal tube by using rag
pieces
AFTER CARE
- Remove rectal tube by using rag
pieces - Discard rag piece in to K-basin
- Place patient comfortably, provide
bedpan if needed - Change linen if soiled, replace
equipment after cleaning - Hand wash and record the procedure in
nurse’s record sheet
HOT APPLICATION & COLD APPLICATION
PATIENT POSITIONING , COMFORT DEVICES
NURSING PROCEDURES LIST CLICK HERE
NURSING IMPORTANT QUESTIONS – CLICK HERE




![First Aid (Quick Study Health) PDF Free Download [Direct Link]](https://bazarbiblio.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/First-Aid-Quick-Study-Health-PDF.jpg)
